How To Calculate The Profitability Of Your Online Store (+ 4 Examples)
Case Studies
So you want to start profit tracking. It can’t be that hard, right?
Well, it really depends on how you go about it. Which type of profit margin are you interested in utilizing? What are you going to use to measure and track your profit margins?
If you haven’t already asked yourself those questions, don’t worry – we answer them all for you right here. Read on to learn all the tricks of the trade for calculating profit margins!
Start your Shopify 14-day trial with FireApps
Did you know Shopify is now accounting for 20% of the e-commerce business.
Over 2200 merchants open their Shopify store everyday and 50% of them have a repeat purchase. Join them today!

3 Types of profit
Wondering how to calculate profit for a small business? It turns out there’s more than one way (say what?!). Don’t panic – it’s not as complicated as you might imagine.
The differences between the 3 types of profit are pretty simple to understand, and each one gives you a slightly different perspective on your business’s financial health. Here are the 3 ways how to calculate your profit margin percentage.
1. Gross profit
Gross profit margin measures how well your business handles costs that are directly related to sales. This is the broadest (and simplest) profitability calculation formula since it only considers the net sales (net revenue) and cost of goods sold (COGS). When someone asks “how do you calculate profit as a percentage of sales”, this is the answer they’re looking for.
2. Operating profit
The operating profit margin formula falls somewhere in between the gross profit margin and the net profit margin. While the gross profit margin only considers production costs in relation to net sales, and the net profit margin considers all costs in relation to net sales, the operating profit margin considers direct and indirect costs or operating the business, including:
- Research
- Marketing
- Administrative expenses
- And so on
The big difference between operating profit margin and net profit margin is that the former doesn’t calculate taxes and interest while the latter does. That’s why operating profit margin is also known as earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT).
3. Net profit
Net profit – or what some may call overall profit margin – is the most ‘complete’ method for calculating profitability. The net profit margin considers each and every expense that’s connected to running a business. Those include:
- Direct costs of sales
- Indirect costs of sales (see below)
- Taxes
- Interest
How to calculate gross profit margin?
You’ll need to first measure two factors that will then be used to calculate your business’s gross profit margin.
1. Net sales – gross revenue less returns, discount, allowances, and so on
2. Production costs – expenses to do with the manufacturing of your products (raw materials, labor, etc.)
Once you have those factors accurately accounted for, you can then plug them into the gross profit margin formula.

How to calculate operating profit margin?
You can think of the operating profit margin formula as ‘building on’ the gross profit margin formula. Essentially, the difference is that you’ll be incorporating more business expenses into the formula so that you can bring your profit margins into clearer focus.
On top of the original factors you used in the gross profit margin formula (revenue and production costs), you’ll include the following factors to calculate your operating profit margin:
- Rent
- Research
- Marketing
- Payroll
- Insurance
- Storage
- And so on
Here’s what the operating profit margin formula looks like:

How to calculate net profit margin?
Last in the progression of profit margin calculations is the net profit margin formula. The same way that the operating margin formula built on the gross margin formula, so the net profit margin formula also builds on the operating margin formula.
To calculate the net profit margin you must include revenue, production costs and total operating expenses in addition to taxes and interest. For the most part, when people speak about how to calculate profitability, what they really want to know is how to calculate the net profit margin.
Look no further! Here’s the formula for calculating your online store’s net profit margin:

How to keep track of profits?
1. Spreadsheets
While they’re pretty clunky and often messy, spreadsheets are a great place to start tracking your online store’s profits. First off, learning how to design a spreadsheet that tracks your profits doubles as a way to familiarize yourself with the equations that we outlined above. By ‘programming’ the spreadsheet on your own or with the help of online resources, you’ll get to know which formulas are important and how they work.
Secondly, spreadsheets keep you involved in the process of tracking your profits. While automated solutions are a dream come true (we get to those just below) they allow you to put the responsibility of calculating your profits in the hands of another. Again, automated profit tracking tools exist for good reasons, but by doing the work for you they also make it easy for you to avoid learning how to do it yourself.
2. BeProfit Profit Tracker app
This is by far the easiest and most efficient way for Shopify and Wix business owners to track their stores’ profits (and expenses for that matter). The BeProfit profit calculator app for Shopify and Wix is overflowing with advanced analytics tools that make it easy to understand and optimize your business’s profitability.
With BeProfit, you have the power to:
- Create and export custom reports
- Track your profit history over time
- Get intuitive visuals and graphs
- Freely edit your store’s data
- Understand complex business metrics
- Connect metrics once with smart integrations
- Spot what factors need improvement to increase profits
- Make data-driven decisions to optimize your store
- Understand complex business metrics
- Connect metrics once with smart integrations
- Spot what factors need improvement to increase profits
- Make data-driven decisions to optimize your store
3. Google Analytics
If you didn’t already know that Google had its tentacles in the business analytics game, allow us to give you the good news. But seriously, Google Analytics is one of the most popular tools that e-commerce business owners use to accurately track and monitor their profits.
It also integrates with many if not most platforms, including top ad platforms, social media platforms, and so on. Where Google Analytics falls a bit short is the complexity of setting it up.
If you wanted to set up a GA dashboard that would calculate your profit as accurately as BeProfit, for instance, it would not be an easy endeavor. You’d have to run through the coding yourself, or find the codes online and paste them into your dashboard, or (if you’re not well-versed in coding) you’d have to hire an expert to do it for you.
Still, Google Analytics should be mentioned simply because of how powerful it is – when done right, it’s an immensely useful tool.
4. Built-in eCommerce dashboards
If you don’t feel like learning how to create spreadsheets for tracking profit, or searching for the ‘right’ third-party app or tool for your business, the good news is that most eCommerce platforms have built-in analytics dashboards.
Since you’re probably logging into your store account multiple times a day, there’s an obvious advantage to having all of your business data available right there in the same platform. It’ll save you some time not having to switch between tabs in your browser, and can save you some money by not having to invest in another app.
On the other hand, there are plenty of limitations that those built-in dashboards have – mostly to do with integrations. That means, for the most part, the average analytics dashboard that you’d find built into an eCommerce platform will lack the depth and detail that you’d find in a third-party app like BeProfit or Google Analytics.
What is a good profit margin?
To answer this question, you’ll need to narrow it down and be more specific. Which industry are you talking about? Which niche? What products are you selling and who are you selling to?
If you want to truly understand whether your online store’s profit margins are good or not, you’ll need to compare it to other businesses working in the same niche. To help you out, we’ve compiled a list of average profit margin examples for some of the top industries (gathered from NYU Stern data). Check it out:
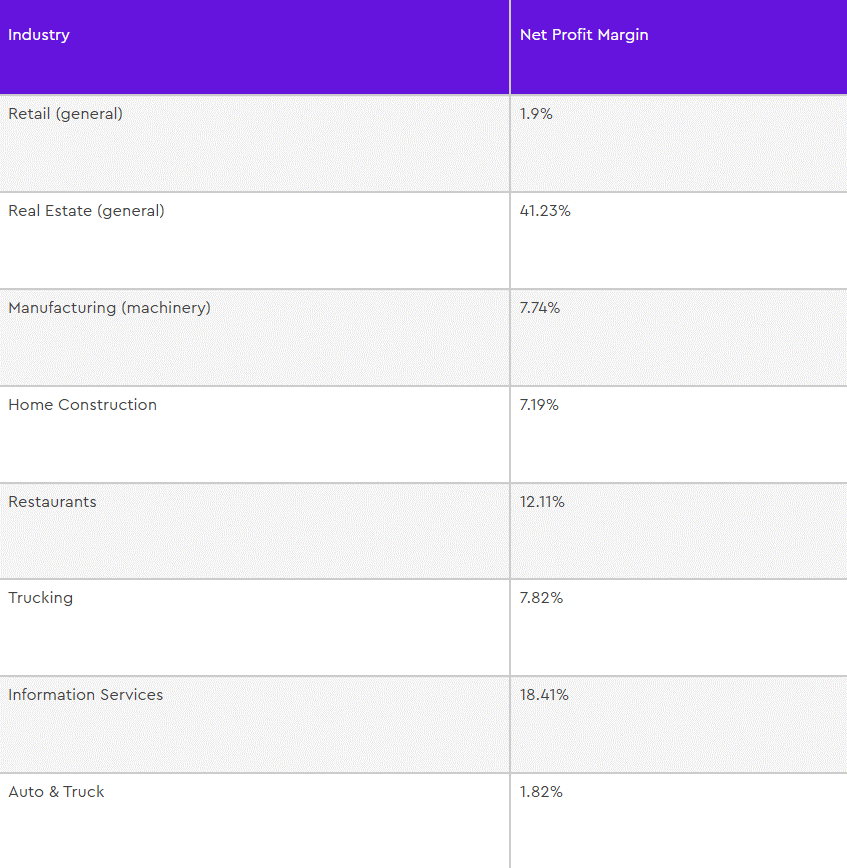
Improving your profit margin
There are countless ways to raise your online store’s profit margins, so take into consideration that the following list is really just the tip of the iceberg. That said, these are some of the best tactics you can use to give your business’s profitability the boost it’s been waiting for.
The best ways to improve your profit margin include:
- Find ways to reduce overhead costs, whether it means replatforming, switching to a different e-commerce business model, etc.
- Focus on customer support as an effective strategy for reducing returns and refunds
- Streamline your supply chain to cut down on supplier rates, prepare for surges in demand, and so on
- Start selling on multiple channels in order to engage with omnichannel customers (they actually spend 10% more on their average purchase than single-channel customers)
Final thoughts
When your business is ‘in the black’ it means it’s profitable. But don’t get that mixed up with you staying ‘in the dark’ when it comes to your profit margins! While we certainly recommend taking full advantage of the automated solutions mentioned in this article, what really matters is that you take the time to understand your profits (regardless of how you do it). The bottom line is this: the importance of calculating your profit margins cannot be overestimated!
Let’s find out more about the world of e-commerce here Fireapps


Leave a Reply